

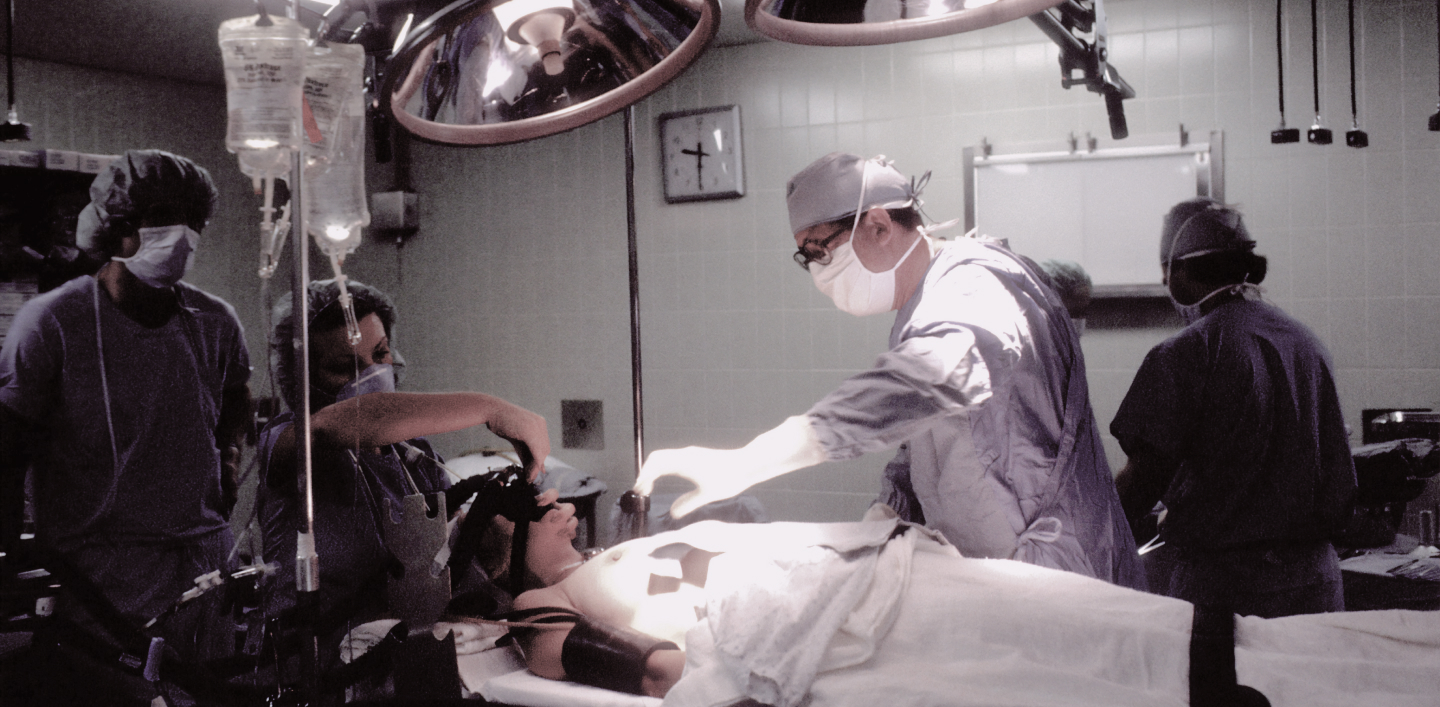
The need of maxillofacial surgery arises in cases of injuries, cracks, fractures, congenital defects, inflammatory pathological conditions, neoplasms of the skull, as well as for complex problems with bite.
Treatment of injuries, deformations and diseases of the face and skull. This surgery is usually performed using specialized tools and technology, such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and X-rays. These methods allow the surgeon to accurately determine the extent of damage and the location of the pathology. Procedures that may be performed by a craniofacial surgeon include bone and tissue reconstruction, tumor removal, trauma rehabilitation, and other surgeries involving the face and skull.

eyes pathology :
eversion of the lower eyelid (ectropion); retraction of the eyelid (too high position of the upper eyelid or too low position of the lower eyelid); violation of the patency of the lacrimal ducts – lacrimal or tear lake, lacrimal or tear stream, lacrimal or tear tubules, lacrimal points, beginning of lacrimal tubules, nasolacrimal duct
orbital injuries (of eyeballs)
salivary gland diseases:
non-neoplastic (sialosis, sialoadenitis – inflammatory, etc.); tumorous (adenoma)
neoplasm in the area of head and neck:
benign cellular – lipodermoid (or dermolipoma, lipoma - a benign formation from adipose tissue in a capsule), osteomas (from bone tissue); vascular hemangioma (from cells of the inner layer of vessels), angioma (from blood vessels), lymphangioma (from lymphatic vessels and spaces); cysts (formations with a capsule filled with mucus, dead cells) – epidermoid (from the surface layer of the skin), dermoid (from the surface and deeper layers of the skin, hair follicles, sebaceous glands); precancerous diseases of the skin of the face and mucous membrane of the lips
purulent-inflammatory processes of head and neck area :
abscess, phlegmon
head and neck fistula
(pathological channel that connects hollow organs to each other or to the body’s surface)
congenital malformations of head and neck area:
appendages of the auricle (growths, tubercles near the auricle), vascular malformations (formations from vessels)
thermal injuries of head and neck (burns and their consequences)
diseases and damage to nerves of maxillofacial area:
neuralgia (pain in the area of the nerve), neuritis of the trigeminal nerve (inflammation), neuritis of the facial nerve (inflammation)
bone defects of the head and neck
post-traumatic deformation of the face (after an injury)
eagle syndrome (Eagle syndrome, styloid syndrome – lengthening of the styloid process of the temporal bone)
these manifestations can be in different locations: on the surface:
infraorbital space, frontal area, orbital zone (eye sockets), paraorbital zone (around the eye sockets), temporal fossa, subtemporal fossa, pterygoid fossa (Bish's fossa), hard and soft palate, chin area, cheek area, submandibular fossa, pterygoid-maxillary space, peripharyngeal space
inside the bones:
front wall of the frontal sinus, orbit walls, frontal complex, lower jaw (mandible) angle and body of lower jaw, condylar process of lower jaw, articular head of lower jaw, temporomandibular joint
If necessary, specialists consult people not only in Ukraine, but also in any country in the world, both in the clinic itself in Kyiv and online by prior appointment. Both diagnostics, treatment and prevention are carried out.


Years of experience
Patients
A modern clinic in the center
Successful operations
Unique surgical techniques
Branch of surgery
Units of the latest equipment
Charitable surgical assistance

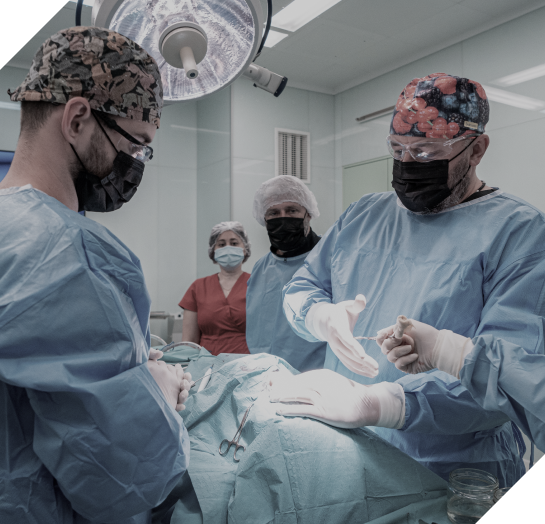
We provide the entire complex of surgical interventions in craniofacial surgery.
During the intervention, we use exclusively modern materials – metal structures, metal osteosynthesis, own biological tissues or tissues of autografts.
We perform both surgical interventions to eliminate the consequences of trauma, as well as oncological operations in the areas of the upper and middle third of the face.
You should contact a craniofacial surgeon as soon as possible if you have the following symptoms:


You should contact a craniofacial surgeon as soon as possible. The consultation includes:
survey (the doctor will ask about complaints, learn about the history of diseases, life)
an external clinical assessment (all changed areas, local lymph nodes, the state of each organ system will be carefully examined, palpated and otherwise investigated)
laboratory examination (both general clinical tests and special tests)
instrumental examination (to determine both the general condition of the body and those parts of it where changes have developed, in particular, X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI))







bougieurage of nasolacrimal canal
removal of dermoid cyst
removal of lipodermoid (dermolipoma)
removal of lateral cyst of neck
removal of the middle cyst of neck
removal of appendages of auricle
plastic closure of head and neck fistulas
removal of neoplasms of the eyelids
removal of vascular malformations of the paraorbital zone
removal of benign neoplasms of the paraorbital zone
opening of paraorbital zone abscess
opening and drainage of abscesses and phlegmon of the infraorbital, buccal, orbital, temporal, subtemporal, pterygoid fossa, hard and soft palate
opening and drainage of abscess and phlegmon of the chin, cheek, submaxillary, pterygoid-maxillary, oropharyngeal spaces
correction of inversion of the lower eyelid
orbital decompression
correction of eyelid retraction of a higher degree of complexity (with cartilage autotransplantation)
correction of eyelid retraction
drainage of tear ducts
reconstruction of orbital walls after injury
open reposition and fixation using metal osteosynthesis of fractures of the upper jaw
open reposition and fixation using metal osteosynthesis of fractures of the lower jaw in the angle and body areas
open reposition and fixation using metal osteosynthesis of the condylar process of the lower jaw
open reposition and fixation of the facial complex
open reposition, osteosynthesis in the area of the articular head
reconstruction of the head of temporomandibular joint
reconstruction of the bones of facial skeleton
repositioning and fixation using metal osteosynthesis of the front wall of the frontal sinus
reconstruction of the walls of the orbit with an individualized implant
surgical treatment of thermal lesions of head and neck
surgical treatment of diseases of temporomandibular joint
surgical treatment of diseases and damage to the nerves of maxillofacial area (neuralgia, trigeminal neuritis, facial neuritis)
treatment of precancerous diseases of the skin of the face and mucous membrane the lips
treatment of birth defects and skin tumors
surgical treatment of tumors and tumor-like formations from adipose tissue
installation of a fabric expander
endoprosthesis of facial areas
endoprosthesis of the angles of the lower jaw
endoprosthesis of the chin
taking a bone autograft from the tibia
taking a bone autograft from the iliac bone
taking a bone autograft from the vault of the skull
collection of fascial autograft
taking a cartilaginous ear autograft
taking a cartilaginous rib autograft
chin augmentation by osteotomy
chin reduction by osteotomy
canthopexy
resection of the upper jaw
resection of the lower jaw
resection of the lower jaw with one-moment reconstruction
resection of the alveolar process
replacement of bone defects in the head and neck area with individualized implants
orthognathic surgery
cystectomy of head and neck cysts
treatment of non-neoplastic diseases of the salivary glands
parotidectomy for adenomas of large salivary glands
surgical treatment of post-traumatic facial deformation
treatment of sialodenitis
treatment of sialosis
replacement of defects of the lower jaw with a titanium implant
placement of a titanium implant in the area of the temporomandibular joint
placement of a combined implant (titanium, peek) in the area of the temporomandibular joint
treatment of Eagle syndrome

in the case of taking any drugs, inform the doctor about it and agree with him (it may be necessary to limit them or change the dose, regimen)
for a few days before the operation, follow a gentle diet, water-drinking regime; if there is constipation, take laxatives, use enemas and do not drink alcoholic beverages – so that the body reacts more adequately and predictably to anesthesia and other drugs
refrain from eating for 6–12 hours before the operation, and for 2–4 hours also do not drink, do not use chewing gum, do not smoke – to prevent stomach contents from entering the respiratory organs during anesthesia
on the day of the operation, take a shower, cleanse the intestines with an enema – so that during anesthesia, due to the relaxation of the sphincters, feces do not come out involuntarily
immediately before the operation:
removable objects (piercing jewelry, prostheses) should be removed from the oral cavity and face – so that during the operation they do not accidentally enter the respiratory organs or interfere with the surgical intervention; remove other items (contact lenses, hearing aids, jewelry) – so that they do not accidentally injure the body and do not get spoiled; cosmetic products (makeup, nail polish, artificial nails) should be removed from the body – to facilitate visual assessment of the body's condition and automated registration using medical equipment; empty the bladder and, if necessary, the intestine – so that this does not happen involuntarily during anesthesia; changing into special clothes, which are given in the clinic
addition, other preparatory measures may be carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism and the specifics of the surgical intervention

The main stages:
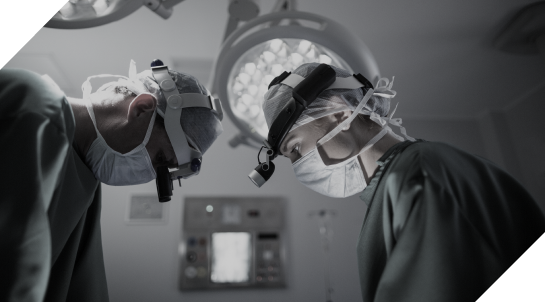

to the operating room on a gurney or escorted on foot. In the airlock room, a medical cap and shoe covers are put on (to prevent microorganisms from entering the air of the operating room).
trauma are performed by an operational team of a certain composition, taking into account the specifics of each operation.
(depending on the specifics of the operation, the position of the body may differ), fixed to it with special straps.
a vein puncture on the hand, installs a catheter to administer the necessary drugs, installs electrodes on the body to monitor the electrical activity of the heart, puts a tonometer cuff on the shoulder, and a sensor to determine the oxygen content in the blood. All this is necessary for continuous monitoring of the body's condition during anesthesia and surgery.
depends on the specific task, the part of the body on which the intervention is carried out, corresponds to the features of the selected surgical tactics, technique.

After surgery, the patient wakes up in the ward for postoperative observation. If necessary, oxygen can be supplied through a thin tube to provide the body with a sufficient amount of oxygen. The nurse will carefully monitor the condition of the body and, if necessary, apply drugs agreed with the doctor.
Before patient’s return home, the doctor will examine the areas where the intervention was performed, agree on the tactics of further rehabilitation, give additional advice.



A craniofacial surgeon deals with the operative treatment of bone injuries, congenital tissue defects, inflammation, neoplasms, and other pathological conditions of the facial skull.
Injuries and diseases of the facial part of the skull are accompanied by the following symptoms, which determine the feasibility of consulting a craniofacial surgeon: bleeding from the ears, mouth, nose; uneven dilation of the pupils; headache, nausea and vomiting; loss of consciousness; volumetric and purulent-inflammatory processes of the skull.
Craniofacial surgery, bone plasty of the face, repositioning of the bones of the facial skull and fixation using metal osteosynthesis is required in cases of: skull injuries, especially with displacement; congenital defects and acquired deformations of bones.
The guarantee for surgical treatment of ENT organs applies to implants and other medical consumables and equipment. The provision of surgical treatment services is guaranteed in accordance with the modern achievements of medicine, the high level of qualification of the clinic’s specialists and the technical equipment of the clinic. The final clinical effect is influenced by many factors that depend not only on the doctor and the hospital – individual characteristics of an organism, its lifestyle, environmental circumstances, stress factors.
Possible complications after craniofacial surgery include general surgical ones (bleeding and thrombosis, infectious-inflammatory conditions, etc.) and more specific to such conditions (postoperative defects, non-union of bones, epileptic syndrome, etc.). Careful preparation for the operation, highly qualified and experienced medical staff, modern high-tech equipment and coordinated work of the medical team and other staff of the clinic minimize the risk of complications.
Relative contraindications for craniofacial operations are the severe condition of the patient and other conditions under which the risk of surgical treatment exceeds the risk of other medical interventions.


