

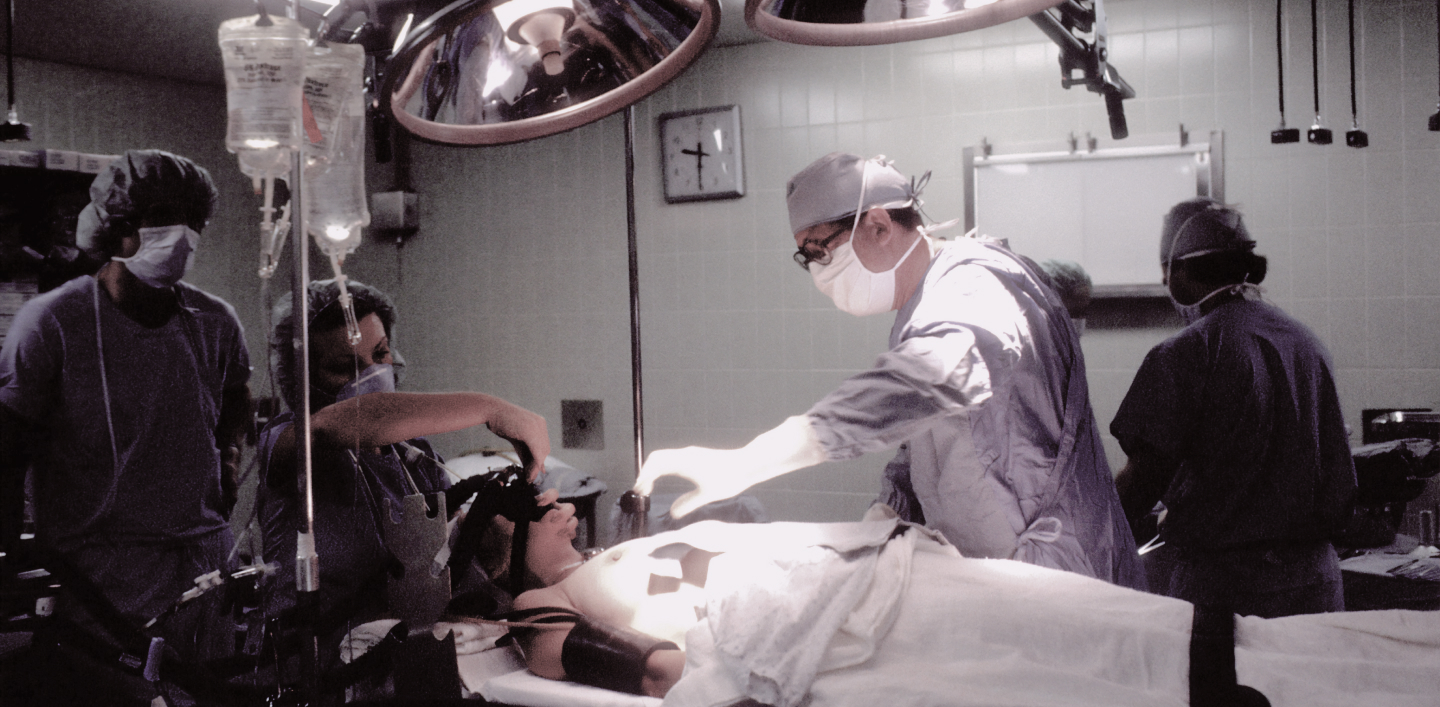
Reconstructive or restorative surgery is a branch of clinical medicine whose main purpose is to correct congenital and acquired body deformities, as well as functional disorders, whether they are genetic or caused by diseases and injuries.
The primary objective of reconstructive (restorative) surgery is to ensure the proper functioning of organs and to achieve aesthetic improvements.
Reconstructive surgical procedures hold significant importance in addressing congenital and acquired bodily defects that can greatly diminish quality of life or even be life-threatening.
This field involves repairing the structure and functions of bodily tissues after damage resulting from trauma, birth anomalies, or oncological conditions. This may encompass the repair of bones, joints, muscles, skin, and organs. Reconstructive surgery aims to enhance patient quality of life and functional well-being.
If required, specialists will provide consultations to residents not only in Ukraine but also from any country around the world, either in-person at the clinic in Kiev or online through scheduled appointments.


Years of experience
Patients
A modern clinic in the center
Successful operations
Unique surgical techniques
Branch of surgery
Units of the latest equipment
Charitable surgical assistance

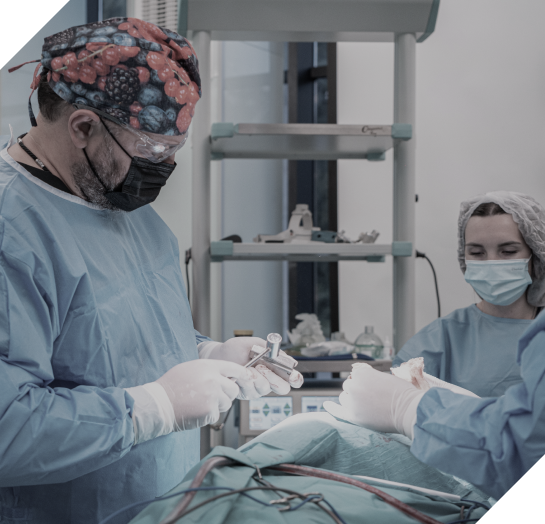
We perform all surgical interventions in accordance with the standards set by the European Association of Reconstructive Surgeons.
We use IPRAS standards
We engage well-known foreign surgeons in all surgical interventions.
We simulate and ensure the outcomes of surgical interventions. We utilize biopolymers and the patient’s own autologous tissues through autografting techniques.
Surgical interventions are carried out with the help of modern techniques of the hardware base of 2021 – these are laser installations, endoscopic, laparoscopic equipment and modern possibilities of growing the patient’s own tissues, in particular skin.
The Valikhnovski Surgery Institute provides assistance in the following situations:
stretch marks and flabby abdomen
deformation of the front abdominal wall
deformation of the eyelids
ptosis of the lower eyelid (drooping)
aesthetically unacceptable corners of the eyes
the need to change the shape of the eye
a wish to remove Bichat's lumps (Bish's, Bisha's) "pouches" – accumulations of dense fatty tissue that form the fatty body of the cheek)
a wish to reproduce the natural shape of the breast
deforming diseases of the mammary gland
state after mastectomy (state after removal of the mammary gland)
the desire to enlarge the mammary glands
a wish to reduce mammary glands
nipple and areola deformation
simple syndactyly (finger fusions)
polydactyly (increased number of fingers)
violation of the ligamentous-capsular apparatus
deformation of the toes
hallux valgus ("bone", "bump" on the leg in the area of the first toe)
valgus deformity of the first finger
deformity of the nose
deformation of the nasal membrane
deformation of the nasal sinuses
deformation of the nostrils
deformation of the back of the nose
deformation of the tip of the nose
the consequences of unsuccessful previous surgical interventions
congenital malformations of the nose
deformation of the nose after removal of tumors and other formations, both malignant and benign
deformation of the nose due to various operations on the face and nasolabial triangle, which led to negative consequences
deformation of the nose after an accident
deformation of the nose after injuries
deformation of the lips
congenital cleft of the upper lip
cleft lip ("harelip")
cleft palate
consequences of bite by an animal
a wish to change the shape and size of the lips
deformation of the auricle
partial loss of the auricle
complete loss of the auricle
congenital deformation of the auricle
deformation of the auricle
flap ear




abdominoplasty
miniabdominoplasty
correction of diastasis recti muscles abdominal muscles with the installation of an Ethicon mesh
surgical correction of sagging abdominal skin
surgical correction of excess weight in the abdominal area
surgical correction of ptosis of the abdominal muscles
lifting of the sagging abdomen after childbirth
lifting of the sagging abdomen after weight loss
surgical removal of stretch marks and abdominal flabbiness,
correction of deformation of the abdominal wall front
blepharoplasty / plastic of eyelids, upper or lower
blepharoplasty / plastic of eyelids, circular
canthopexy
lateral canthoplasty
surgical treatment of the lower eyelid ptosis
surgical change in the position of the eyes corners
change in the shape of the eye by the surgical method
removing of Bichat’s lumps (Bish’s, Bisha’s) “pouches” – accumulations of dense fatty tissue that form the fatty body of the cheek)
reconstruction for the purpose of reproduction natural breast shape
one-moment breast reconstruction using one’s own tissues
one-moment reconstruction using implants
combined reconstruction (includes both of the above methods)
flap breast reconstruction
organ-preserving plastic surgery for mammary gland disease
reconstructive breast plastic surgery after mastectomy with a rotational flap of the latissimus dorsi muscle
breast reconstruction after mastectomy
reconstructive operations after breast removal
augmentation with vertical mastopexy
breast augmentation with mastopexy in the form of an inverted “T”
breast augmentation with periareolar mastopexy
breast augmentation through axillary access (anatomical implants)
breast reconstruction using “Polytech” implants
breast reconstruction by using “Eurosilicone” implants
reconstruction of mammary glands using “Motiva” implants
reconstruction of mammary glands using “Mentor” implants
reconstruction mammary gland surgery with the help of expanders
breast enlargement through an incision around the areola
breast reduction with a vertical scar
reconstructive mammoplasty
nipple and areola
lift vertical (without the cost of consumables)
breast lift in the form of an inverted “T”
reconstruction in case of simple syndactyly
reconstruction in case of polydactyly
reconstruction of ligament-capsular apparatus
hand reconstruction in case of congenital extra toe
reconstruction of leg in case of congenital extra toe
reconstructive plastic surgery in case of toe deformity
reconstructive plastic surgery for hallux valgus
reconstruction of valgus deformity of the 1st toe
reconstructive rhinoplasty
reconstructive septoplasty
reconstruction of nasal sinuses
reconstruction of nostrils
reconstruction of nasal septum
reconstructive plastic surgery of the nasal bridge
reconstructive plastic surgery of the nose tip
reconstruction of the nose after unsuccessful previous surgical interventions
reconstruction of the nose due to congenital malformations of the nose
reconstruction after removal of tumors and other formations, both malignant and benign
reconstruction of the nose due to various operations on the face and nasolabial triangle, which led to negative consequences
reconstruction of the nose after an accident
reconstruction of the nose after injuries
reconstructive cheiloplasty
primary cheiloplasty according to E. V . Gotsko
reconstructive cheiloplasty for congenital cleft lip
reconstructive lip plasty in case of cleft lip (“harelip”)
reconstructive lip plasty in case of cleft lip
reconstructive lip plasty in case of bite by an animal
reconstructive lip plasty with changes in shape and size
lipofilling of lip
lip reconstruction using the “bullhorn” technique
lip reconstruction using the “corner-lift” technique
lip reconstruction using the “V-Y plasty” technique
reconstruction of auricle
reconstruction after partial loss of auricle
reconstruction after complete loss of auricle
reconstruction of congenital deformity of auricle
reconstructive plastic surgery of the auricle
reconstructive ear plastic surgery in case of protruding ears
reconstruction of the auricle by the method of its formation from neighboring tissues
reconstruction of the auricle with the help of costal cartilage
reconstruction of the auricle by the formation of a frame made from autologous cartilage

in the case of taking any drugs, inform the doctor about it and agree with him (it may be necessary to limit them or change the dose, regimen)
for a few days before the operation, follow a gentle diet, water-drinking regime; if there is constipation, take laxatives, use enemas and do not drink alcoholic beverages – so that the body reacts more adequately and predictably to anesthesia and other drugs
refrain from eating for 6–12 hours before the operation, and for 2–4 hours also do not drink, do not use chewing gum, do not smoke – to prevent stomach contents from entering the respiratory organs during anesthesia
on the day of the operation, take a shower, cleanse the intestines with an enema – so that during anesthesia, due to the relaxation of the sphincters, feces do not come out involuntarily
immediately before the operation :
removable objects (piercing jewelry, prostheses) should be removed from the oral cavity and face – so that during the operation they do not accidentally enter the respiratory organs or interfere with the surgical intervention; remove other items (contact lenses, hearing aids, jewelry, etc.) – so that they do not accidentally injure the body and do not get spoiled; cosmetic products (makeup, nail polish, artificial nails) should be removed from the body – to facilitate visual assessment of the body's condition and automated registration using medical equipment; empty the bladder and, if necessary, the intestine – so that this does not happen involuntarily during anesthesia; changing into special clothes, which are given in the clinic
addition, other preparatory measures may be carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism and the specifics of the surgical intervention

The main stages:


or escorted on foot. In the airlock room, a medical cap and shoe covers are put on (to prevent microorganisms from entering the air of the operating room)
by an operational team of a certain composition, taking into account the specifics of each operation
(depending on the specifics of the operation, the position of the body may differ), fixed to it with special straps
performs a vein puncture on the hand, installs a catheter to administer the necessary drugs, installs electrodes on the body to monitor the electrical activity of the heart, puts a tonometer cuff on the shoulder, and a sensor to determine the oxygen level in the blood. All this is necessary for continuous monitoring of the body's condition during anesthesia and surgery
depends on the specific task, the part of the body on which the intervention is carried out, corresponds to the features of the selected surgical tactics, technique

After surgery, the patient awakens in the postoperative observation ward. If necessary, oxygen can be administered through a slender tube to ensure an adequate oxygen supply to the body. The nurse will diligently monitor the patient’s condition and, if needed, administer medications as approved by the doctor.
Prior to the patient’s discharge, the doctor will assess the sites where the procedure was conducted, collaborate on a plan for ongoing rehabilitation, and provide additional guidance.



Reconstructive surgery is a specialized field of clinical medicine that focuses on restoring the structure and functionality of congenital or acquired, deformed, or lost body parts. Traditionally, plastic surgery aims to correct defects, while reconstructive surgery is concerned with the restoration of body parts. In reality, these two disciplines share a significant overlap and are often integrated into procedures known as reconstructive plastic surgery operations.
The duration and number of stages of reconstructive surgery vary depending on each individual case – ranging from a few tens of minutes to a much longer period.
The guarantee for reconstructive surgery pertains to the accurate execution of services, advanced diagnostic procedures, treatment, highly qualified specialists, implants, and other necessary medical supplies and equipment.
Before deciding to undergo reconstructive surgery, thorough laboratory and instrumental studies should be carried out. The results of these studies will help ensure the proper condition of the body and the safety of the surgical treatment.
Possible complications after reconstructive surgeries may include bleeding, thrombosis, infectious and inflammatory conditions, cosmetic defects, and more. Careful preparation for the operation, highly qualified and experienced medical staff, modern high-tech equipment, and the coordinated work of the medical team and other clinic staff help minimize the risk of complications.
Contraindications for reconstructive operations are conditions in which the severity significantly increases the risks associated with surgical treatment. Examples of such conditions include infectious diseases, mental disorders, gastrointestinal issues, and more.


