

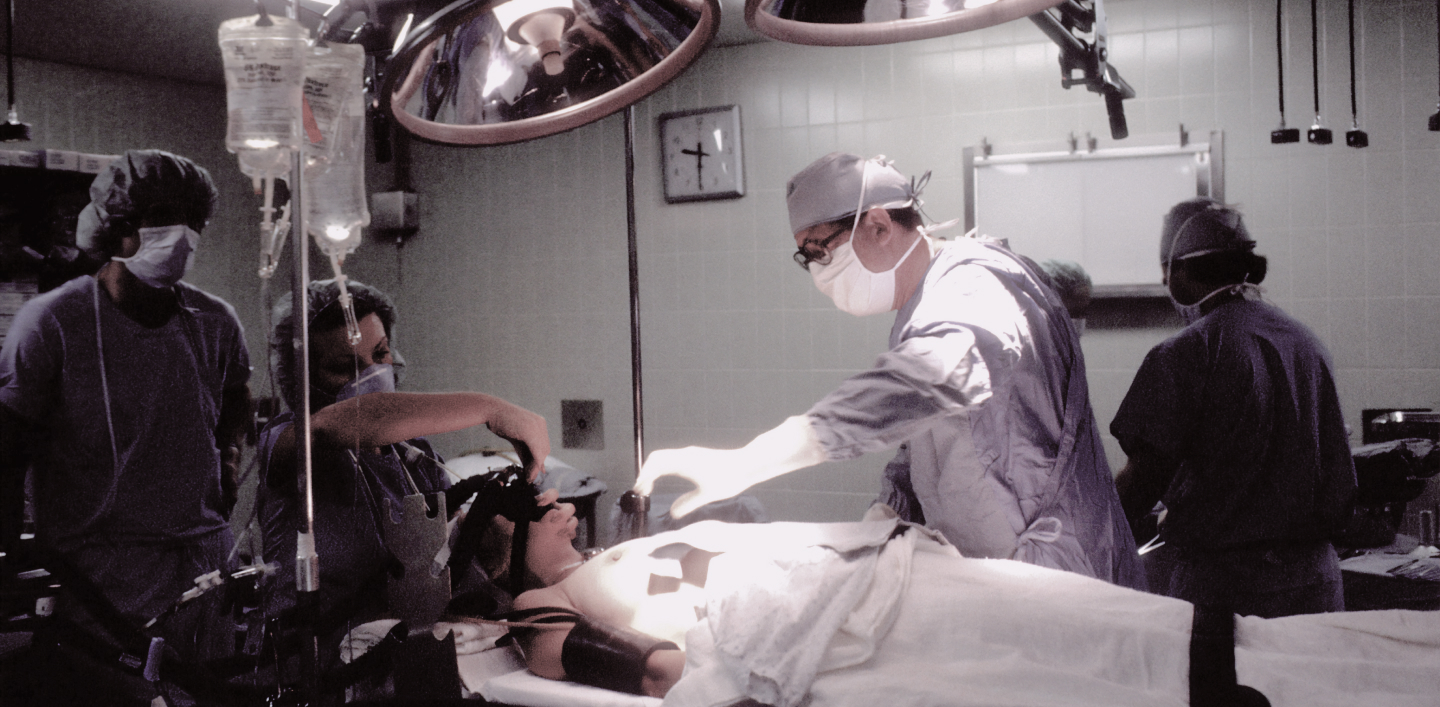
The issue of emergency surgery arises in cases of severe, critical conditions that threaten life and health and require immediate diagnosis and surgery.
Emergency surgery is performed on an emergency or urgent basis, in peacetime or wartime.
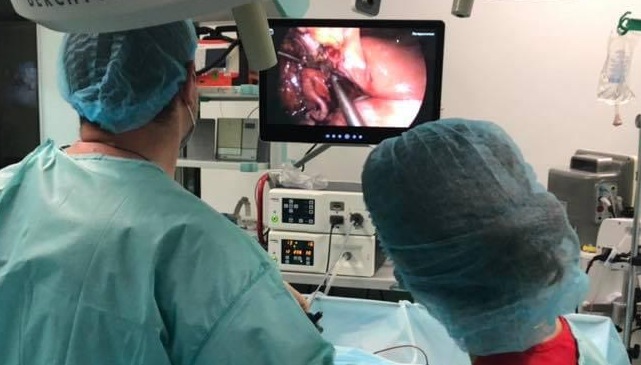
Emergency surgery is usually performed using specialized technologies, such as resuscitation and intensive care, and other instrumental and laboratory parameters, if necessary. This allows the doctor to accurately determine the nature of the disorder and provide appropriate emergency surgical care. Special equipment allows performing emergency surgical interventions with minimal damage to surrounding tissues (endoscopically, laparoscopically or laparotomically), in particular, single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS).
Timely and properly provided emergency surgical care allows patients to return to normal life and maintain or restore its quality.

If needed, our doctors provide consultations not only in Ukraine but also worldwide, both at our clinic in Kyiv and online through prior appointments. Comprehensive diagnostics, treatment, and prevention are offered.


Years of experience
Patients
A modern clinic in the center
Successful operations
Unique surgical techniques
Branch of surgery
Units of the latest equipment
Charitable surgical assistance
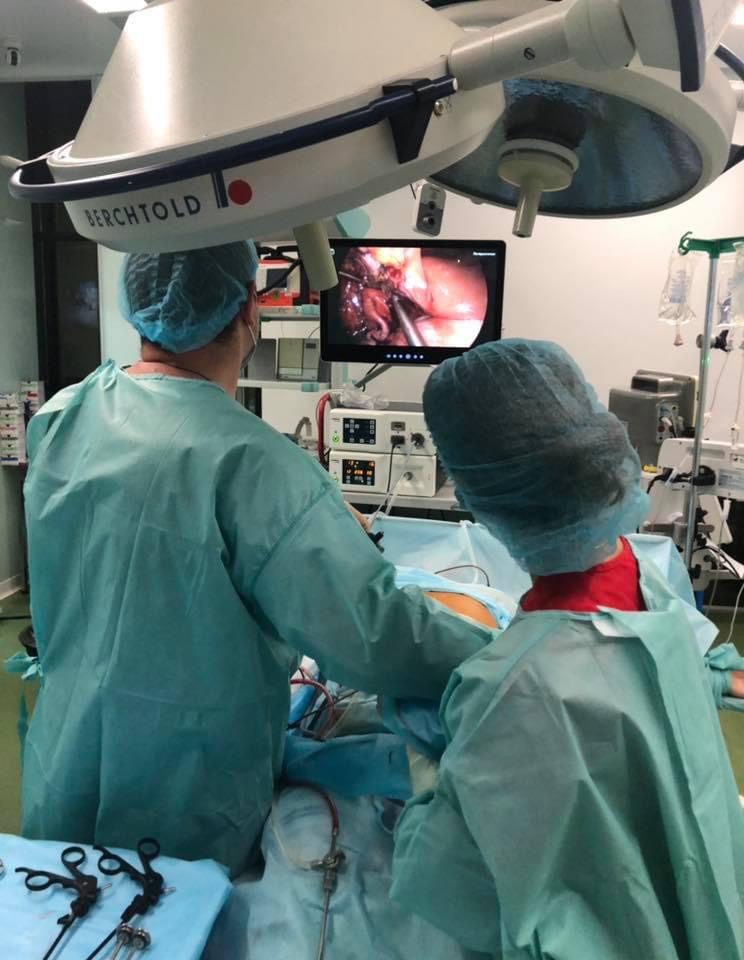
You should promptly consult regarding emergency surgery if you experience the following symptoms:

A consultation in emergency surgery includes:
interview (the doctor asks about complaints, learns about medical history and life)
external clinical assessment (the patient will be thoroughly examined, palpated, all altered areas and the condition of each organ system will be examined)
laboratory examination (both general clinical tests and special tests)
instrumental examination (to determine both the general condition of the body and those areas where changes have developed).








in case of taking any medications, inform your doctor and agree with him/her (it may be necessary to limit them or change the dosage or regimen);
before the operation, follow a sparing diet, water and drinking regimen and do not drink alcoholic beverages - so that the body reacts more adequately and predictably to anesthesia and other drugs
refrain from eating for 6-12 hours before the operation, and do not drink, chewing gum, or smoke for 2-4 hours before the operation to protect against the ingestion of stomach contents into the respiratory system during anesthesia, etc
if possible, before the operation, take a shower or otherwise hygienize the body, cleanse the intestines with an enema to prevent spontaneous passage of feces during anesthesia due to sphincter relaxation
immediately before the operation –
- removable objects (piercing jewelry, dentures) are removed from the oral cavity and face so that they do not accidentally get into the respiratory system or interfere with the surgical intervention during the operation
- remove other items (contact lenses, hearing aids, jewelry, etc.) to prevent accidental injury to the body and to prevent them from getting damaged
- remove cosmetics (makeup, nail polish, false nails) from the body to facilitate visual assessment of the body's condition and automated registration with medical equipment
- empty the bladder and, if necessary, the intestines to prevent spontaneous bowel movements during anesthesia
change into special clothes provided by the clinic
Other preparatory measures can be taken in addition, taking into account individual characteristics of the body and the specifics of the surgical intervention

The main stages:

or escorted on foot. At the gateway, they put on a medical cap and shoe covers (to protect against microorganisms in the air of the operating room).
of a certain composition, taking into account the specifics of each operation.
(depending on the specifics of the operation, the body position may differ), and fixed to it with special straps to prevent accidental involuntary movements that would interfere with the operation, as well as to prevent accidental falling of the body from the table.
installs a catheter to administer the necessary drugs, places electrodes on the body to monitor the electrical activity of the heart, puts a blood pressure cuff on the shoulder and a sensor on the finger to determine the oxygen content in the blood. All this is necessary for continuous monitoring of the body's condition during anesthesia and surgery.
the area of the body where the intervention is performed, and the specifics of the chosen surgical tactics, technique, etc

After the operation, the patient wakes up in the ward for postoperative observation. If necessary, oxygen may be administered through a thin tube to ensure that the body has enough oxygen. The nurse will carefully monitor the patient’s condition and, if necessary, use medications agreed with the doctor.
Before returning home, the doctor will examine the postoperative sutures, agree on the tactics of further rehabilitation, and give additional advice.



Emergency surgical medical care is provided for symptoms such as sharp, attack-like and growing abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting without relief, fever, changes in the color of urine and feces, palpitations, pale skin, low blood pressure, a sharp decrease in urination, bloody impurities in the urine, sudden deterioration of the condition against the background of a chronic disease or injury.
Most often, emergency surgery is required for the following pathological conditions and diseases acute cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, acute intestinal obstruction, acute appendicitis, perforation of gastric and duodenal ulcers, penetration of gastric and duodenal ulcers peritonitis, strangulated hernia (hernia), internal bleeding, acute urinary retention, ectopic pregnancy, pathological labor, acute paraproctitis, severe hemorrhoidal bleeding.
In the practice of emergency surgery, X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), pulse oximetry, ultrasound, electrocardiography (ECG), surgical intervention (surgery), resuscitation, intensive care, anesthesia, oxygen therapy and other methods are used.
The surgical team for emergency surgical care usually consists of an operating physician, a surgical nurse, an anesthesiologist, and an anesthesia nurse. In specific cases, the team may be supplemented by other surgeons and surgical nurses and subspecialists depending on the clinical situation.
For the safety of patients, we use sterile medical equipment, ensure compliance with hygiene standards in the premises, carefully follow medical protocols and standards.
The guarantee for the results of emergency surgery applies to medical consumables and equipment. It guarantees the provision of emergency surgical medical care in accordance with modern medical advances, the high level of qualification of the clinic’s specialists and the technical equipment of the clinic. The final clinical effect is influenced by many factors that depend not only on the doctor and the clinic, such as individual characteristics of the body, lifestyle, environmental conditions, and other factors.


