

The Mammology Center of the Valikhnovski Surgery Institute clinic performs surgical operations on the mammary gland that allow for the restoration or improvement of breast appearance, as well as the treatment of diseases affecting this organ.
Situations in which you should consider breast surgery include:
Breast cancer, also known as mammary gland cancer, breast oncology, or mammary gland oncology, arises due to genetic changes (mutations) in the cells of the glandular tissue, milk duct walls, and occasionally other tissues. These changes lead to the development of malignant tumors. Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer, affecting about one in twelve women globally. If not treated in a timely and appropriate manner, it can become the leading cause of death among women due to oncological diseases, according to the World Health Organization.
Current life-saving surgical treatment for breast cancer is usually combined with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. The primary method involves surgically removing the tumor and reconstructing the breast.

Intraductal carcinoma in situ
- cancer within the ducts of the mammary gland's surface layer without spreading elsewhere.
invasive ductal carcinoma
- cancer in the mammary gland ducts that has penetrated other layers.
Lobular (partial) carcinoma in situ
- cancer within the breast's glandular tissue lobes without spreading elsewhere.
Invasive lobular (partial) carcinoma
- cancer in the glandular tissue of the breast lobes that has penetrated other parts of the organ.
Paget's disease
- cancer of the nipple and/or areola of the mammary gland.
Tubular carcinoma
- a ductal cancer type with single-layer tube-formed cells surrounded by fibers.
Inflammatory breast cancer
- a tumor type where cancer cells block small lymphatic channels in the breast, leading to inflammation.
Nipple cancer
- tumor location in the nipple tissues.
HER-2 positive subtype of breast cancer
- a tumor type where the HER-2 gene is active, leading to resistance of cancer cells to certain drugs.
Luminal A subtype of breast cancer
hormone-dependent tumor type that relies on progestin and estrogen and is HER-2 negative.
Luminal B subtype of breast cancer
- hormone-dependent tumor type relying on progestin and estrogen and being HER-2 positive.
Consultations with doctors are available not only in Ukraine but also internationally, either at the Kyiv clinic or online by appointment. Comprehensive diagnostics, treatment, and preventive measures are provided.


Years of experience
Patients
A modern clinic in the center
Successful operations
Unique surgical techniques
Branch of surgery
Units of the latest equipment
Charitable surgical assistance

All necessary interventions (tumor removal, replacement, implant installation) are performed at once, and not in several stages.

The patient does not need a second surgical intervention, the entire operation is performed simultaneously according to the standards of the association of mammologists of Europe.

Minimum number of scars.
Hospital stay 2 days, postoperative rehabilitation – 7 days
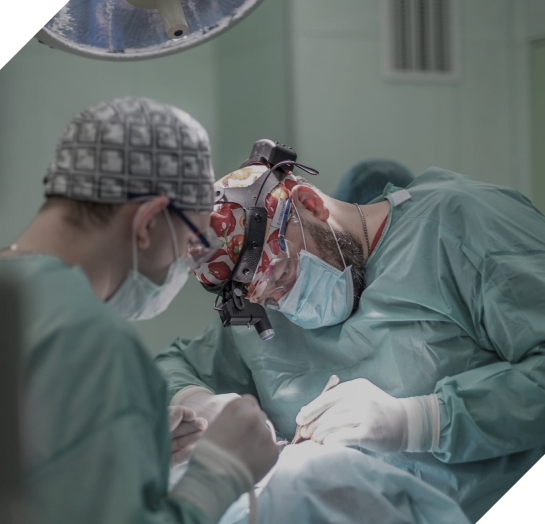
The primary method of modern breast cancer treatment is surgery.
Additionally, radiation therapy, pharmaceuticals, and a wide range of supplementary treatment and prevention methods are employed.
Numerous options for breast cancer surgery exist. Contemporary surgical approaches prioritize minimally invasive methods and organ-preserving procedures.
These surgeries have distinct selection criteria, varying procedural techniques, as well as indications and contraindications, taking into account the stage, growth characteristics, and metastasis of the cancer.
For instance, key indications for oncoplastic surgery on the mammary gland include:


The surgeon's consultation includes:
Survey (the doctor will ask about complaints, learn about the history of diseases, life);
An external clinical assessment (all changed areas, local lymph nodes, the state of each organ system will be carefully examined, palpated and otherwise investigated);
Laboratory examination (both general clinical tests and special tests);
Instrumental examination (to determine both the general condition of the body and those parts of it where changes have developed, in particular, computer (CT), magnetic resonance (MRI) tomography);







Primary operations on the mammary gland, such as breast reconstruction to restore natural shape, inverted “T” breast lift, and reduction mastopexy to remove excess glandular volume and achieve surgical tightening and reduction.
Endoprosthesis of mammary glands – an operation to increase or change their volume, shape, or correct asymmetry using synthetic fillers.
Symmetrizing vertical mastopexy of a healthy mammary gland – an operation to achieve identical, symmetrical breasts.
Minimally invasive surgery of the mammary gland without a scalpel or anesthesia – puncture treatment of acute purulent lactating (or non-lactating) mastitis under ultrasound guidance, followed by flow-washing drainage.
Axillary lymph node dissection (ALD) – an operation involving the axillary lymph nodes.
Biopsy of the sentinel (or signal) lymph node (BSLN) – a lymph node is selected, removed, and examined for the presence of breast cancer cells, serving as a sample.
Quadrantectomy – partial removal (resection) of the mammary gland, involving the tumor and surrounding normal tissues, along with regional lymph nodes.
Various mastectomy procedures – Patey mastectomy (removal of the mammary gland with axillary tissue and pectoralis minor muscle), Madden mastectomy (removal of the mammary gland with axillary tissue, excluding pectoralis major and minor muscles), modified radical mastectomy (less traumatic and more cosmetic and functionally acceptable than classical mastectomy).
Oncoplastic lumpectomy procedures with various techniques, such as vertical mammoplasty, T-shaped mammoplasty, plastic areola restoration, utilizing different approaches to preserve the gland while removing the pathology.
Simple lumpectomy – removal of a fragment of breast tissue within the tumor.
Radical mastectomy procedures, including axillary lymphodissection or biopsy of the sentinel lymph node, involve complete removal of the mammary gland along with fatty tissue, fascia, and pectoralis major and minor pectoral muscles.

One-time breast reconstruction using autologous tissues – this involves breast flap reconstruction, where a skin-muscle flap is taken from other parts of the body (such as the stomach, back, buttocks).
One-time breast reconstruction using a TRAM flap – a flap of the anterior abdominal wall is employed for breast reconstruction (transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap, which is a transverse skin-muscular flap based on the rectus abdominis muscle).
One-time breast reconstruction using a thoraco-dorsal flap – a skin-muscle flap is taken based on the latissimus dorsi muscle for breast reconstruction.
One-time breast reconstruction using a gluteal flap – a skin-muscular flap is taken from the large gluteal muscle for breast reconstruction.
One-time reconstruction with the use of implants – breast reconstruction surgery utilizing implants (implants that allow shaping of the desired form).

The main stages:

on a gurney or escorted on foot. In the airlock room, a medical cap and shoe covers are put on (to prevent microorganisms from entering the air of the operating room).
of a certain composition, taking into account the specifics of each operation.
(depending on the specifics of the operation, the position of the body may differ), fixed to it with special straps.
installs a catheter to administer the necessary drugs, installs electrodes on the body to monitor the electrical activity of the heart, puts a tonometer cuff on the shoulder, and a sensor to determine the oxygen content in the blood. All this is necessary for continuous monitoring of the body's condition during anesthesia and surgery.
the part of the body on which the intervention is carried out, corresponds to the features of the selected surgical tactics, technique.
Preparation for facial procedures follows general principles for surgical interventions:
If taking any medications, inform the doctor and obtain their guidance (adjustments to medication usage or dosages may be necessary);
Adhere to a mild diet and proper water intake in the days leading up to the operation. If constipated, consider laxatives or enemas, and abstain from alcohol consumption. This ensures a more stable and predictable response to anesthesia and other medications;
Abstain from eating for 6–12 hours before the procedure. In the 2–4 hours preceding the surgery, refrain from drinking, chewing gum, or smoking to minimize the risk of stomach contents entering the respiratory system during anesthesia.
On the operation day, take a shower and use an enema to cleanse the intestines. This prevents involuntary fecal discharge during anesthesia due to sphincter relaxation.
Immediately before the procedure:
– Remove removable objects (piercing jewelry, prostheses) from the oral cavity and face to prevent accidental entry into the respiratory tract or interference with the surgical process.
Remove other items (contact lenses, hearing aids, jewelry) to prevent accidental bodily injury and damage;
– Remove cosmetic products (makeup, nail polish, artificial nails) from the body to facilitate visual assessment and automated monitoring using medical equipment;
– Empty the bladder and, if necessary, the intestines, to prevent involuntary discharge during anesthesia;
– Change into the provided clinic-issued special clothing;
Depending on individual characteristics and the specific surgery, additional preparatory measures may be undertaken.
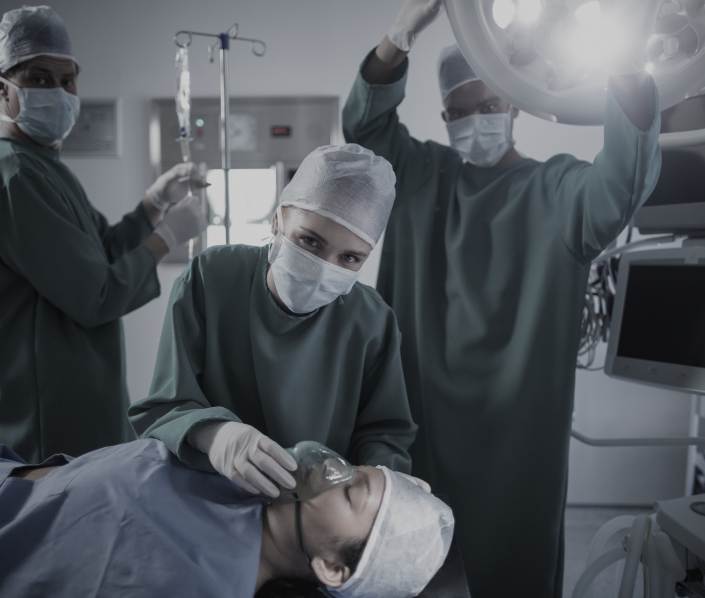
For aesthetic purposes, in particular, after previously performed operations on the mammary gland, the following can be performed:
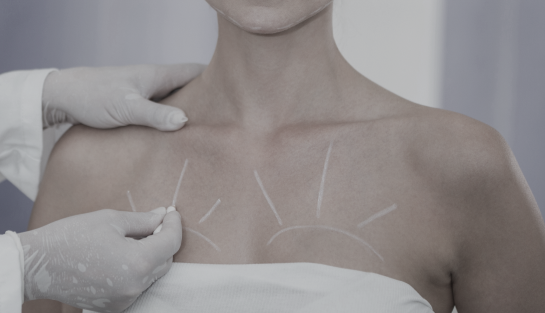
Lifting of the mammary glands and avoiding their sagging

Introduction of an implant under the mammary gland in order to give the breast an aesthetic appearance

After surgery, the patient wakes up in the ward for postoperative observation. If necessary, oxygen can be supplied through a thin tube to provide the body with a sufficient amount of oxygen. The nurse will carefully monitor the condition of the body and, if necessary, apply drugs agreed with the doctor.
Before patient’s return home, the doctor will examine the areas where the intervention was performed, agree on the tactics of further rehabilitation, give additional advice.



Breast surgery may be warranted for conditions accompanied by symptoms such as:
These and other symptoms can be associated with a variety of breast conditions, including benign formations (e. g., fibroadenomas, cysts) as well as breast cancer. If you notice any of these symptoms or have any questions or concerns, it is important to see a breast doctor or plastic surgeon for a detailed examination and proper medical advice. Early diagnosis and treatment can be the key to a successful recovery for any breast problems.
It is important to remember when the first problems started and, if possible, write them down for yourself so that you don’t forget anything, noting any bothersome symptoms. At the consultation, take with you all medical documentation, all preliminary examination results. But it is not worthwhile to specifically undergo new ones, since the doctor himself will write out a referral, if necessary.
If there are no urgent reasons, it is better to choose the time after the expiration of menses and before the onset of ovulation. But if you notice a discharge from the nipple, feel pain in the breast or find a thickening, etc., then it is better to see a doctor on any day, regardless of the phase of the cycle.
In surgery, there are several methods of mastopexy and mammoplasty. The choice of method depends on the individual characteristics of the woman, such as the shape of the breast, the degree of deformities or expectations after surgery, the peculiarities of the anatomy and physiology of the body and other factors. Using exactly endoprosthesis to create the necessary volume is justified if the breast has a lot of skin but little tissue.
In the vast majority of operations mastopexy, mammoplasty, both with artificial implants and without, do not affect breastfeeding and can be performed before pregnancy. However, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, the mammary glands undergo such significant transformations that repeated aesthetic surgery may be required, so it is justified to give birth and nurse the baby first, and perform breast surgery later.
Neoplasms, tumors of the mammary gland (in particular, cancer) can be located in different places of the organ and, taking this into account, look different. Due to the location in the depth of the gland, there may be no external manifestations at all (unless the compaction is determined by palpation), and if it is in the area of the nipple, it is deformed, compacted.
In general, with rare exceptions, pain is not a characteristic manifestation of breast cancer. But, due to the growth of tumor tissue, there may be a feeling of distension, swelling and other discomfort up to pain.
Unnatural discharge from the nipple (bloody or transparent), deformation of the nipple, change in the shape of the skin of the breast (such as unusual folds, wrinkles), non-healing ulcers, swelling, discomfort (tension, distension to the point of pain), enlargement of regional lymph nodes (under the armpits) etc. For metastases – signs of damage to the corresponding organs (lungs, liver, bones, brain).
Potentially – yes, any breast cancer is curable, at least if it is diagnosed in time and adequate treatment is applied.
The guarantee for surgical treatment applies to implants and other medical consumables and equipment. The provision of surgical treatment services is guaranteed in accordance with the modern achievements of medicine, the high level of qualification of the clinic’s specialists and the technical equipment of the clinic. The final clinical effect is influenced by many factors that depend not only on the doctor and the hospital – individual characteristics of an organism, lifestyle, environmental circumstances, stress factors.


