

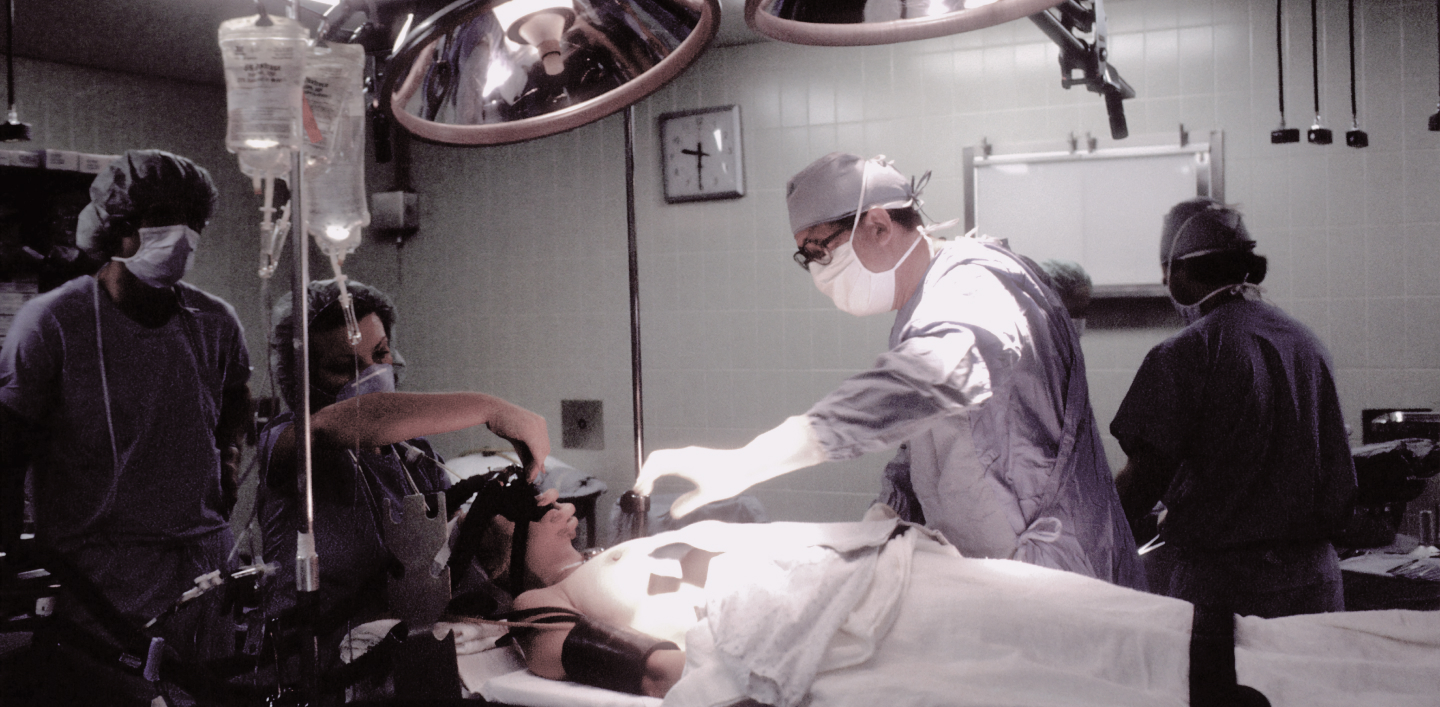
Maxillofacial surgery is a branch of clinical medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of various diseases, pathological conditions, anomalies in the areas of the head (mainly the face, jaws, oral cavity) and neck.
Treatment of injuries, deformations and diseases of the jaws, face and adjacent tissues. This surgery is usually performed using microscopes, endoscopes, and other specialized tools that allow the surgeon to work with precision and minimal damage to the surrounding tissue. Procedures that may be performed by a maxillofacial surgeon include correcting malocclusion, repairing broken bones, and removing tumors.

atypical location of the tooth
knocked out teeth
periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum – the surface layer of bones)
jaw cyst
sequestra (fragments of dead tissue)
neoplasms of the oral cavity or the surface of the skin
dislocation of the lower jaw
jaw fractures
fistula of the upper jaw
benign neoplasm of the jaws (odontoma – from the main tissue of the tooth, cementoma – from the cementum of the tooth)
stone of the duct of the submandibular salivary gland
stone of the submandibular salivary gland
osteogenic tumors and tumor-like formations of the jaws
connective tissue tumors of the jaws
vascular tumors of the jaws
Bish’s lumps
neoplasms of the oral cavity
retained (out-of-set) tooth of the jaw
retained wisdom tooth on the upper jaw
retained wisdom tooth on the lower jaw
dislocated (incorrectly located) wisdom tooth
orthodontic conditions that require correction
retention cyst of the sublingual salivary gland
retention cyst of small salivary glands
dislocation of the lower jaw
violation of the integrity of the facial complex
bilateral cleft of the alveolar bud of the upper jaw
unilateral cleft of the alveolar bud of the upper jaw
congenital cleft of the soft and partially hard palate
connection between the oral cavity and maxillary sinus (oro-antral connection)
pathology of the frenulum of the tongue
pathology of frenulum of the lip
surface abscess or phlegmon of the maxillofacial area
furuncle, atheroma in the stage of inflammation on the face
defects and deformations of the palate
violation of bite and profile
sinusitis caused by inflammation in the tooth
difficult eruption of wisdom teeth
inflammatory diseases of the soft tissues of the face caused by inflammation of the teeth
lack of teeth, which requires total implantation
peri-implantitis
recession of the gums (lowering of the edge of the gums, exposure of the teeth)
If necessary, the doctors consult people not only in Ukraine, but also in any country in the world, both in the clinic itself in Kyiv and online by prior appointment.


Years of experience
Patients
A modern clinic in the center
Successful operations
Unique surgical techniques
Branch of surgery
Units of the latest equipment
Charitable surgical assistance

All surgical interventions in the specified area are modulated before the operation due to photo modeling and 3D printing.
We perform the entire necessary set of surgical interventions at the same time.
We actively cooperate with partner clinics in implantology.

Maxillofacial surgeon should be contacted as soon as possible if the following symptoms develop:


The consultation includes:
a survey (the doctor will ask about complaints, learn about the history of diseases, life)
an external clinical assessment (all changed areas, local lymph nodes, the state of each organ system will be carefully examined, palpated and otherwise investigated)
laboratory examination (both general clinical tests and special tests)
instrumental examination (to determine both the general condition of the body and those parts of it where changes have developed, in particular, X-ray computer tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) tomography)







atypical tooth removal
smoothing the edges of the tooth socket (alveolectomy)
tooth-preserving operations (hemisection, root amputation, coronary-radicular separation)
tooth replantation
surgical treatment of periostitis (periostomy)
jaw cyst removal
sequestration removal (sequestrectomy)
removal of a neoplasm of the oral cavity or skin surface
closed reposition of the lower jaw
splinting jaws using IMF screws
plastic and closing fistulas of the upper jaw area
plastic and closing fistulas of the upper jaw
removal of benign neoplasms of the jaws (odontoma, cementoma)
removal of submandibular salivary gland duct stone
removal of submandibular salivary gland stone (together with the gland)
treatment of osteogenic tumors and tumor-like formations jaws
treatment of connective tissue tumors jaws
treatment of vascular tumors of the jaws
removal of Bisha lumps
removal of neoplasms of the oral cavity
removal of a retained (out-of-set) tooth of the jaws
removal of a retained wisdom tooth on the upper jaw
removal of a retained wisdom tooth on the lower jaw
removal of a dystopian (incorrectly positioned) wisdom tooth
removal of a tooth for orthodontic indications
gentle maxillary sinusectomy
removal of a retention cyst of the sublingual salivary gland
removal of a retention cyst of the minor salivary glands
reduction of dislocation of the lower jaw
closed reposition of the cheek complex without fixation
bone plastic of a bilateral cleft alveolar ridge of the upper jaw
bone plastic of unilateral cleft alveolar ridge of the upper jaw
plastic of congenital cleft of the soft and partially hard palate
necroectomy of the jaw
plastic closure of the connection between the oral cavity and maxillary sinus (oro-antral connection)
plastic surgery of tongue frenulum
plastic surgery of lip frenulum
opening of superficial abscess or phlegmon of the maxillofacial area
opening of furuncle, atheroma in the stage of inflammation on the face
installation of dental implants
elimination of defects and deformations of the palate
surgical correction bite and profile
treatment of sinusitis caused by inflammation in the tooth
treatment of difficult eruption of wisdom teeth
treatment of inflammatory diseases of the soft tissues of the face caused by inflammation of the teeth
jaw implantation
one-moment implantation
delayed implantation
two-stage implantation
installation of a gum former
installation of an abutment
installation of a mini implant
removal of a disintegrating implant
treatment of peri-implantitis
bone block transplantation
zygomatic tooth implantation (Zygoma)
implantation using a navigation template (minimally invasive)
lengthening of the crown part of the tooth
bone augmentation
vestibuloplasty
plasma lifting
open sinus lifting
closed sinus lifting
bone grafting of the alveolar process of the jaw
taking an autograft from the chin
taking an autograft from the mental part of the jaw
taking an autograft from the branch of the lower jaw
mucogingival surgery
treatment gum recession,

in the case of taking any drugs, inform the doctor about it and agree with him (it may be necessary to limit them or change the dose, regimen)
for a few days before the operation, follow a gentle diet, water-drinking regime; if there is constipation, take laxatives, use enemas and do not drink alcoholic beverages – so that the body reacts more adequately and predictably to anesthesia and other drugs
refrain from eating for 6–12 hours before the operation, and for 2–4 hours also do not drink, do not use chewing gum, do not smoke – to prevent stomach contents from entering the respiratory organs during anesthesia
on the day of the operation, take a shower, cleanse the intestines with an enema – so that during anesthesia, due to the relaxation of the sphincters, feces do not come out involuntarily
immediately before the operation:
removable objects (piercing jewelry, prostheses) should be removed from the oral cavity and face – so that during the operation they do not accidentally enter the respiratory organs or interfere with the surgical intervention; remove other items (contact lenses, hearing aids, jewelry) – so that they do not accidentally injure the body and do not get spoiled; cosmetic products (makeup, nail polish, artificial nails) should be removed from the body – to facilitate visual assessment of the body's condition and automated registration using medical equipment; empty the bladder and, if necessary, the intestine – so that this does not happen involuntarily during anesthesia; changing into special clothes, which are given in the clinic
addition, other preparatory measures may be carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism and the specifics of the surgical intervention

The main stages:
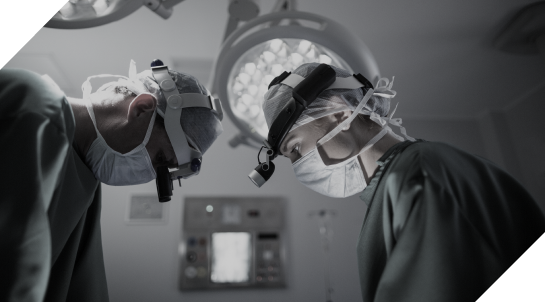

or escorted on foot. In the airlock room, a medical cap and shoe covers are put on (to prevent microorganisms from entering the air of the operating room).
of a certain composition, taking into account the specifics of each operation
(depending on the specifics of the operation, the position of the body may differ), fixed to it with special straps.
a vein puncture on the hand, installs a catheter to administer the necessary drugs, installs electrodes on the body to monitor the electrical activity of the heart, puts a tonometer cuff on the shoulder, and a sensor to determine the oxygen content in the blood. All this is necessary for continuous monitoring of the body's condition during anesthesia and surgery.
depends on the specific task, the part of the body on which the intervention is carried out, corresponds to the features of the selected surgical tactics, technique.

After surgery, the patient wakes up in the ward for postoperative observation. If necessary, oxygen can be supplied through a thin tube to provide the body with a sufficient amount of oxygen. The nurse will carefully monitor the condition of the body and, if necessary, apply drugs agreed with the doctor.
Before patient’s return home, the doctor will examine the areas where the intervention was performed, agree on the tactics of further rehabilitation, give additional advice.



Maxillofacial surgeon treats pathologies of the bones of the facial skeleton: congenital defects, acquired defects (cracks, fractures, other injuries), inflammatory diseases, neoplasms, etc. A specialist can not only restore the functionality lost due to a pathological condition, but also recreate the appearance.
A maxillofacial surgeon consult in case of: pronounced injuries in the face area, persistent pain (constant or during chewing, biting), local swelling, bleeding, bite disorders after injuries in the absence of an effect from orthodontic treatment, etc. Jaw surgery may be performed. Maxillofacial surgery and maxillofacial traumatology deal with this.
The guarantee for surgical treatment of the jaw refers to the proper performance of services, high-tech diagnostics, treatment, high qualification of specialists, implants and other medical consumables and equipment.
Preparation for operations on the maxillofacial area includes a preliminary examination and consultation by a maxillofacial surgeon, a comprehensive examination, with photo and video analysis of appearance, anthropometry, consultation of related specialists (if necessary), etc. Immediately before the operation, the principles of preparation do not differ significantly from those generally accepted in surgery.
Possible complications after surgery include general surgical ones (bleeding and thrombosis, infectious-inflammatory conditions, etc.) and more specific to this field (postoperative defects, non-union of bones, etc.). Careful preparation for the operation, highly qualified and experienced medical staff, modern high-tech equipment and coordinated work of the medical team and other staff of the clinic minimize the risk of complications.
Contraindications to maxillofacial surgery are conditions, the severity of which critically increases the risks of surgical treatment, for example, infectious, mental, gastrointestinal diseases.


