

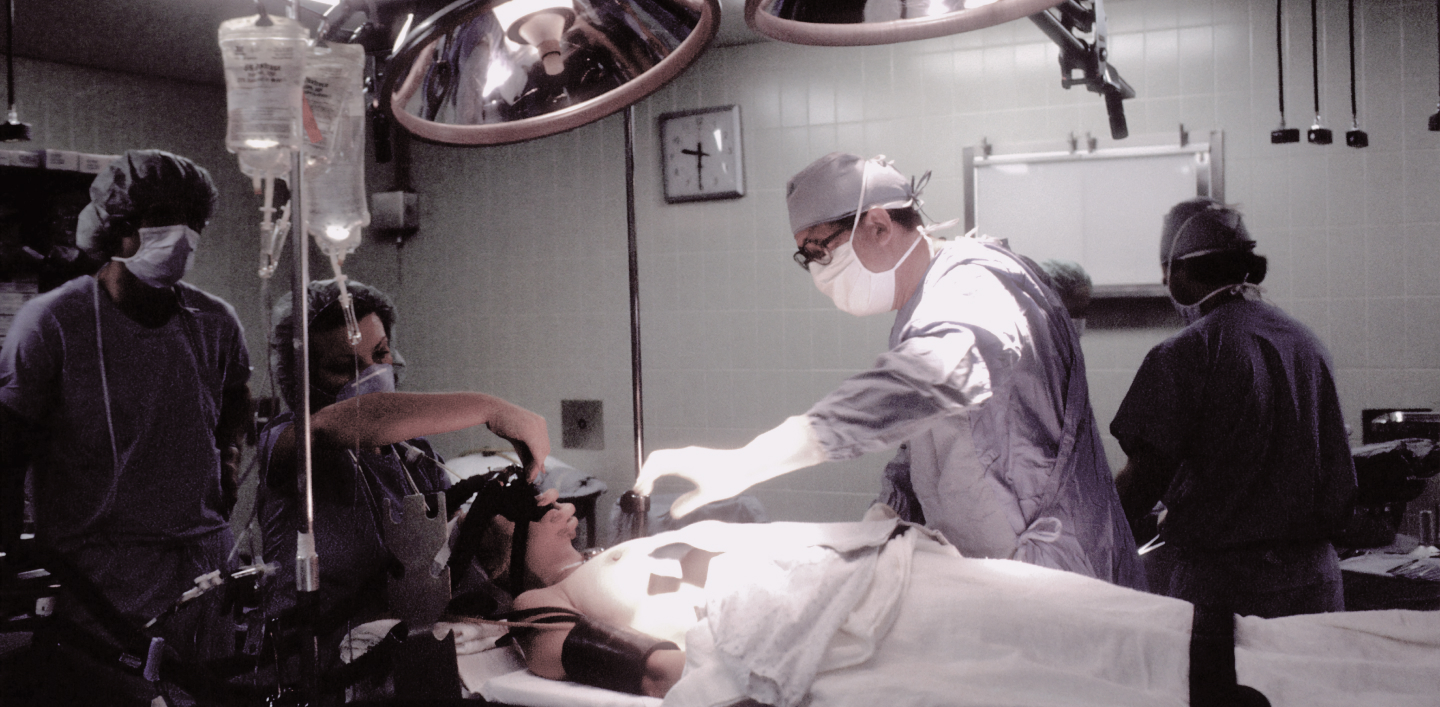
Surgical intervention for neoplasms in the areas of the head and neck consists in the physical removal of tumors of the corresponding location (head tumors, tumors іn neck).
This branch of surgery that specializes in the treatment of tumors and other diseases of the head and neck. This technique is used to treat various types of cancer, such as thyroid cancer, palatine tonsil cancer, nasopharyngeal cancer, and others.
During head and neck cancer surgery, surgeons remove tumors located in the head and neck using a variety of techniques. These methods may include radical extirpation, which involves removing all visible signs of the tumor, and resection, which removes part of the tumor to reduce its size and facilitate further treatment.
Head and neck cancer surgery involves the use of a variety of technologies, such as microscopic and endoscopic surgery, that allow surgeons to see and remove tumors while reducing the risk of damage to surrounding tissue. In addition, this technique may include other procedures, such as radiotherapy and chemotherapy, which provide additional treatment and reduce the risk of recurrence of tumors. Head and neck oncology surgery is an effective method of treating head and neck tumors, allowing patients to return to normal life after the procedure.

tumors of the oral cavity
neoplasm of the neck area
neoplasms of connective and other soft tissues of head, face, neck
carcinoma in the neck and head area (a tumor that originates from the deepest layer of the skin)
chemodectoma (a tumor that originates from tissues that secrete hormones or hormone-like substances and react to changes in concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood)
neoplasms of connective and other soft tissues of the face
tumors of the submandibular salivary gland
neoplasms of connective and other soft tissues of the neck
tumor of jaw
hemolymphangioma of the face (a vascular neoplasm of a mixed structure, which contains both blood and lymphatic vessels)
jaw myxoma (a benign tumor that originates from bone cells)
papilloma of the mucous membrane of oral cavity and lips (a tumor that originates from the surface layers of the skin)
malignant neoplasm of salivary glands
metastases of the neck area (fragments of tumors from another original location)
carcinoma of the nasopharynx
lymphoepithelioma of nasopharynx (the so-called Schminke tumor, which originates from the surface layer of the mucous membrane and is mostly located in the area of the tonsils)
teratoma of head and neck (a congenital tumor that originates from embryonic tissues and develops as a result of a violation of embryonic development)
adenocarcinoma of head and neck (tumor that originates from integumentary and glandular cells)
squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsils
glottic, subglottic and supraglottic cancer (located, respectively, in the larynx, below and above it)
adenoid cystic carcinoma (cancer that forms cavities – cysts)
mucoepidermoid carcinoma (which in particular secretes mucus and keratin)
melanoma of the upper respiratory tract (a tumor that originates from melanocytes – cells that contain dark pigment)
lymphoma of the upper respiratory tract (a tumor that originates from hematopoietic tissue)
If necessary, the doctors consult people not only in Ukraine, but also in any country in the world, both in the clinic itself in Kyiv and online by prior appointment.


Years of experience
Patients
A modern clinic in the center
Successful operations
Unique surgical techniques
Branch of surgery
Units of the latest equipment
Charitable surgical assistance

All surgical interventions are carried out simultaneously – we remove the tumor with the replacement of all tissues, both hard and soft tissues of the head and neck.
Before the operation, we carry out photo modeling of the future result.
During the operation, we use both endoscopic and laser techniques.
We guarantee the results of face reconstruction surgery, as we use implants printed on our own 3D printer, after a CT scan of the head and neck
Any of the manifestations lasting several weeks or more should cause suspicion, especially in people who have serious chronic diseases, smoke, abuse alcohol or drugs. Contact specialists with head and neck neoplasms (especially head and neck cancer) should be treated as early as possible.
It is necessary to consult a doctor for the following main complaints and manifestations:


The consultation includes:
a survey (the doctor will ask about complaints, learn about the history of diseases, life)
an external clinical assessment (all changed areas, local lymph nodes, the state of each organ system will be carefully examined, palpated and otherwise investigated)
laboratory examination (both general clinical tests and special ones, in particular with the study of specific tumor markers - substances that allow assessing the probability of tumor development)
instrumental examination (to determine both the general condition of the body and those parts of it where changes have developed, in particular, X-ray (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission (PET) tomography, etc.)
biopsy of changed tissues (taking a small piece of a neoplasm in order to find out exactly what it is and how to treat it better)







removal of tumors of the oral cavity
removal of neck tumors
removal of the neck endoexpander (a special "bubble" placed under the tissues to be stretched and gradually filled with liquid)
removal of neoplasms of connective and other soft tissues of the head, face, and neck
excision of a neoplasm of soft tissues of the parapharyngeal region (around the pharynx)
removal of basal cell carcinoma in the neck and head area
removal of lip with resection of lower jaw (with cutting out a fragment of the lower jaw bone)
removal of a chemodectoma (a tumor that originates from tissues that secrete hormones or hormone-like substances and react to changes in the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood)
removal of neoplasms of connective and other tissues of the face
removal of submandibular salivary gland tumors
removal of neoplasms of connective and other soft tissues of neck
scalp tumor removal with various options of one-moment plastic surgery
jaw tumor removal
removal of hemolymphangioma of face (vascular neoplasm of mixed structure, which contains both blood and lymphatic vessels)
removal of jaw myxoma (a benign tumor originating from bone cells)
removal of a papilloma of the mucous membrane of oral cavity and lips (a tumor originating from the surface layers of the skin)
removal of malignant neoplasms of salivary glands
removal of neck metastases
removal of lymph nodes and tissue of the neck (useful for widespread location of tumor cells)
hemiglossectomy (partial or complete tongue removal)
glossectomy (complete tongue removal)
hemiglossectomy with microsurgical plastic surgery
hemiglossectomy with a reconstructive-plastic component
endoscopic resection of the larynx (removal of larynx or its part with the help of endoscopic (Greek endon – inside, scopeo – look) tools that allow the surgeon to see everything from inside and use surgical techniques)
combined glossectomy with resection of jaw and floor of mouth with the creation of an orostomy (removal of the tongue, part of the jaw bone and tissues of mouth floor and artificial formation of an opening instead of mouth)
combined resections of tumors of tongue, oropharynx and oral cavity with reconstruction of postoperative defect with displaced flaps on the vascular pedicle or free flaps
combined resections of tongue tumors with reconstruction of the postoperative defect with displaced flaps on vascular pedicle
combined resections of oropharyngeal tumors with reconstruction of the postoperative defect with displaced flaps on vascular pedicle
combined resections of tumors of oral cavity with reconstruction of the postoperative defect with displaced flaps on vascular pedicle
laryngopharyngectomy with reconstruction with a replaced flap (removal of larynx and pharynx with tissue flap restoration from other parts of the body)
applying a tracheostomy (artificial opening of trachea on the surface of the body)
orofacial resection with orostomy formation (removal of a part of face with a mouth opening and artificial formation of the opening instead)
surgery for the radical removal of a tumor of the maxillofacial area with simultaneous reconstruction and restoration of basic functions (simultaneous complete removal of the tumor on the face and restoration of the appearance and function of the organs in this area)
surgery for radical removal of a neck tumor with simultaneous reconstruction and restoration of basic functions (simultaneous complete removal of a tumor in the neck area and restoration of the appearance and function of organs)
Krail's operation (excision of the subcutaneous tissue of the neck together with all its formations, in particular, lymph nodes)
one-time combined resections of tumors of tongue, oropharynx and oral cavity with reconstruction of the postoperative defect with displaced flaps on the vascular pedicle
tongue resection (complete or partial removal)
extended cervical lymphadenectomy (removal of cervical lymph nodes along with other nearby affected structures)
reconstruction of the facial skull using autologous tissues and biocompatible materials (restoration using own tissues, mainly fresh bone and skin-muscle flaps as the "gold standard", as well as titanium, polymer, composite materials, etc., which are not only non-accepted by the body as foreign, but also stimulate the formation of own tissues)
resection of the lower jaw (partial or complete removal)
resection of the upper jaw (partial or complete removal)
wedge-shaped lip resection (partial or complete removal)
square-shaped lip resection (partial or complete removal)
cheek resection (partial or complete removal)
resection of larynx (partial or complete removal)
resection of larynx horizontal (partial or complete removal)
anterior-lateral resection of larynx (partial or complete removal)
resection of the upper jaw with a reconstructive-plastic component (partial or complete removal with restoration of shape and function)
resection of the upper jaw with microsurgical plastic surgery (partial or complete removal with microsurgical restoration of shape and function)
extended radical cervical lymphodissection (complete removal of all cervical lymphatic nodes, optionally with adjacent affected tissues)
subtotal resection of the lip with one-moment plastic surgery (almost complete removal of the lip with simultaneous restoration of its shape and function)
total laryngectomy (complete removal of larynx)
laryngopharyngeal ectomia with reconstruction with a replaced flap (removal of larynx and pharynx with restoration of structures with flaps of own tissues)
surgical treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
surgical treatment of nasopharyngeal lymphoepithelioma
surgical treatment of head and neck teratoma
surgical treatment of head and neck adenocarcinoma
surgical treatment of squamous cell tonsil cancer
surgical treatment of glottic, subglottic and supraglottic cancer
surgical treatment of adenoid cystic carcinoma
surgical treatment of mucoepidermoid carcinoma
surgical treatment of melanoma of upper respiratory tract
surgical treatment of upper respiratory tract lymphoma

in the case of taking any drugs, inform the doctor about it and agree with him (it may be necessary to limit them or change the dose, regimen)
for a few days before the operation, follow a gentle diet, water-drinking regime; if there is constipation, take laxatives, use enemas and do not drink alcoholic beverages – so that the body reacts more adequately and predictably to anesthesia and other drugs
refrain from eating for 6–12 hours before the operation, and for 2–4 hours also do not drink, do not use chewing gum, do not smoke – to prevent stomach contents from entering the respiratory organs during anesthesia
on the day of the operation, take a shower, cleanse the intestines with an enema – so that during anesthesia, due to the relaxation of the sphincters, feces do not come out involuntarily
immediately before the operation :
removable objects (piercing jewelry, prostheses) should be removed from the oral cavity and face – so that during the operation they do not accidentally enter the respiratory organs or interfere with the surgical intervention; remove other items (contact lenses, hearing aids, jewelry, etc.) – so that they do not accidentally injure the body and do not get spoiled; cosmetic products (makeup, nail polish, artificial nails) should be removed from the body – to facilitate visual assessment of the body's condition and automated registration using medical equipment; empty the bladder and, if necessary, the intestine – so that this does not happen involuntarily during anesthesia; changing into special clothes, which are given in the clinic
addition, other preparatory measures may be carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism and the specifics of the surgical intervention

Main stages:

The patient is either brought to the operating room on a gurney or escorted on foot. In the airlock room, a medical cap and shoe covers are put on (to prevent microorganisms from entering the air of the operating room).
Operations related to combat trauma are performed by an operational team of a certain composition, taking into account the specifics of each operation.
The patient is placed on the operating table (depending on the specifics of the operation, the position of the body may differ), fixed to it with special straps.
The anesthetist's nurse performs a vein puncture on the hand, installs a catheter to administer the necessary drugs, installs electrodes on the body to monitor the electrical activity of the heart, puts a tonometer cuff on the shoulder, and a sensor to determine the oxygen content in the blood. All this is necessary for continuous monitoring of the body's condition during anesthesia and surgery.
The further course of the operation depends on the specific task, the part of the body on which the intervention is carried out, corresponds to the features of the selected surgical tactics, technique, etc.

After surgery, the patient wakes up in the ward for postoperative observation. If necessary, oxygen can be supplied through a thin tube to provide the body with a sufficient amount of oxygen. The nurse will carefully monitor the condition of the body and, if necessary, apply drugs agreed with the doctor.
Before the patient’s return home, the doctor will examine the areas where the intervention was performed, agree on the tactics of further rehabilitation, give additional advice.



“Head cancer” is not a specific definition, because tumor may be located in a variety of places on the surface and inside the head, originate from different tissues, and also have different rates and nature of growth, additional properties, etc. General symptoms for cancer are: headache, nausea and vomiting, impaired sensitivity and speech, general weakness, etc., and local symptoms are tissue deformation, volumetric formation in the body, organ dysfunction, etc.
In a case of localization in the neck, tumors cause a cosmetic defect, may be accompanied by erosion and ulcers, dysfunction of local organs, and are also accompanied by general symptoms of cancer (from the whole body).
The guarantee for surgical treatment of head and neck tumors refers to the proper performance of services, high-tech diagnostics, treatment, high qualification of specialists, implants and other medical consumables and equipment. As with any other oncological pathology, the prognosis and guarantees of success of surgical treatment of head and neck tumors largely depend on timely diagnosis, histological type of tumors, background state of health. In terms of technics, all operations in the clinic of Valikhnovski Surgery Institute are performed at the highest world level!
General signs of malignancy of tumors are: loss of functions in cells that they performed before; uncontrollable growth and spread into the surrounding tissues, as well as with the flow of lymph and blood – throughout the body (metastases), dysfunction of the source organ and others. When tumors are located on the head and neck, this is especially dangerous due to the close location of the brain, the tumor damage to which is critical to life.
After operations, classic complications are bleeding or, conversely, thrombosis; impaired function of damaged nerves (sensitivity, movements), secondary infectious and inflammatory processes, etc. In the delayed period of oncological pathology, there is also a risk of relapse (repetition) of tumor growth, partly this may be a consequence of incomplete removal of tumor cells – that is why surgical treatment of tumors is often combined with the use of radiation and chemotherapy, etc.
The key principle in determining of contraindications for any operation, particularly for head and neck tumors, is that the risk of surgery is greater than the risk of other methods.


